728x90
반응형
[정적지시문]
using static System.Console;System.Console 클래스를 using static 과 함께 지정한 후에는 본문에서
Console.WriteLine() 대신 WriteLine()을 직접 사용할 수 있다.
[예제1]
랜덤함수
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
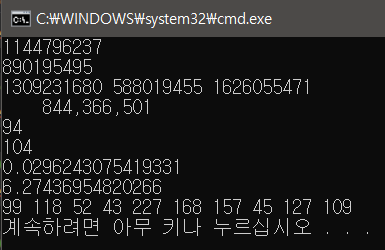
// 4장
//new 키워드와 생성자를 이용해서 Random 타입의 객체를 생성합니다
Random rand = new Random(); // 랜덤클래스 객체를 생성하는 방법
// ex1)
int num = rand.Next(); // 임의의 랜덤한 숫자를 num 의 넣는다. (min이상, max미만)
WriteLine(num);
// ex2)
WriteLine(rand.Next());
// ex3)
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Write(rand.Next() + " ");
}WriteLine();
// ex4)
WriteLine("{0, 15:N0}", rand.Next());
// ex5) 0 ~ 100
WriteLine(rand.Next(100 + 1));
// ex6) 50 ~ 100
WriteLine(rand.Next(50 + 101));
// ex7) 0.0 ~ 1.0 >> color(0,255)
WriteLine(rand.NextDouble());
// ex8) 0.0 ~ 10.0
WriteLine(rand.NextDouble()*10);
// ex9) n개의 랜덤 데이터 생성
byte[] ar = new byte[10];
rand.NextBytes(ar);
foreach(var item in ar)
{
Write(item + " ");
}WriteLine();
}
}
}
[예제2]
전/후위 연산자
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 산술 > (대소)관계 > 논리
if (true && false)
{
}
// 산술연산자 : + - * / %
int a = 0;
int b;
a++;
++a;
b = a++; // 사용증가
b = ++a;
WriteLine("-----------------후위연산자----------------");
a = 10;
WriteLine(a++);
WriteLine(a);
WriteLine("-----------------전위연산자----------------");
a = 10;
WriteLine(++a);
WriteLine(a);
WriteLine("-----------------전후위연산자--------------");
a = 10;
f1(a++); // 10출력
a = 10;
f1(++a); // 11출력
WriteLine("---------------------조심------------------");
// 조심
a = 10;
if (true || ++a > 10)
{
WriteLine(a);
}
}
static void f1(int num)
{
WriteLine(num);
}
}
}

[예제3]
문자열 결합(숫자 + 문자열)
> < >= <= == !=
//ex)
WriteLine(3 > 2);[예제4]
논리연산
논리 연산 (&&, ||, !)
A && B A || B
0 0 0 0
0 1 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1[예제5]
자주 사용하는 논리
bool c = true;
int d = 0;
int e = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
c = !c; // true, false 반전
d = 1 - d; // 0, 1 토글
e = -e; // +1. -1 토글
}[예제6]
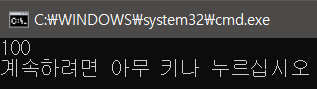
삼항연산
int f = (3 > 2) ? 100 : 200;
WriteLine(f);3이 2보다, 참이면 100, 거짓이면 200
[예제7]
?.(elvis: null 조건분 연산)
1. null 아니면 멤버값이 반환된다.
2. 반환되기 때문에 대입을 받을수는 없다.
3. 반환값이 null일 수 있기 때문에 받는 변수도 ?(elvis)문법을 사용해야 한다.
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? tt;
Foo foo1 = null;
if (foo1 != null)
{
tt = foo1.num;
}
Foo foo2 = null;
// 동일문장
tt = foo2?.num;
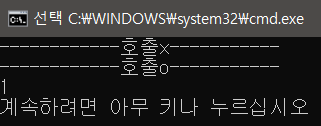
// null 이기 때문에 f1()을 호출하지 않는다.
WriteLine("------------호출x-----------");
foo2?.f1();
WriteLine("------------호출o-----------");
foo2 = new Foo();
// null이 아니기 때문에 f1() 호출
foo2?.f1();
}
class Foo
{
public int num;
public void f1()
{
WriteLine(1);
}
}
}
}
[예제8]
16진수를 2진수로 바꾸기
[배열o]
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void f1(int num)
{
int q = num;
int[] r = new int[100];
int count = 0;
while (q != 0)
{
r[count++] = q % 2;
q = q / 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (i % 4 == 0)
Write(" ");
Write("{0}", r[count - i]);
}
WriteLine("0");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
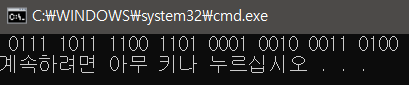
// 0111 1011 1100 1101 0001 0010 0011 0100
int n = 0x7bcd1234;
f1(n);
}
}
}
[배열x]
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void f1(uint num)
{
int check;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
check = 1 << (31 - i);
if (i % 4 == 0 && i != 0)
Write(" ");
Write((num & check) == 0 ? 0 : 1);
}
WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
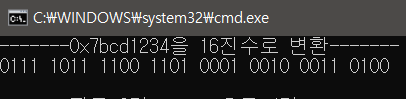
// 0111 1011 1100 1101 0001 0010 0011 0100
WriteLine("-------0x7bcd1234을 16진수로 변환-------");
uint n = 0x7bcd1234;
f1(n);
}
}
}
[예제9]
비트연산
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void f1(uint num)
{
int check;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
check = 1 << (31 - i);
if (i % 4 == 0 && i != 0)
Write(" ");
Write((num & check) == 0 ? 0 : 1);
}
WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 0111 1011 1100 1101 0001 0010 0011 0100
WriteLine("-------0x7bcd1234을 16진수로 변환-------");
uint n = 0x7bcd1234;
f1(n);
WriteLine();
WriteLine("-------좌로 3칸-------우로 4칸-----------");
uint a = n << 3;
f1(a);
uint b = n >> 4;
f1(b);
WriteLine();
WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
uint c = 10;
uint d = c << 4; // 의미: c * 2^4 = c * 16 = 160
uint e = c * 16; // 의미: c를 16번 더한다
WriteLine(d);
uint f = c * 2021;
// 1024 + 512 + 256 + 128 + 64+ 32 + 4 + 1
uint g = (c << 10) + (c << 9) + (c << 8) +
(c << 7) + (c << 6) + (c << 5) + (c << 2) + (c << 0);
WriteLine(g);
WriteLine();
WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
n = 0x7bcd1234;
uint h = n & 0x000fff00; // fff: 내가 알고 싶은 부분
f1(h);
WriteLine();
WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
uint j1 = 0x00000001; // 비트가 상태값을 가진다
uint j2 = 0x00040000;
uint j3 = 0x00040000;
uint j4 = j1 | j2 | j3;
uint j5 = j1 + j2 + j3;
f1(j4);
f1(j5);
n = 0x7bcd1234;
uint k = ~n;
WriteLine();
WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
f1(n);
f1(k);
WriteLine();
WriteLine("------------------XOR------------------");
/* a b
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0 */
uint l = n ^ 0xffffffff;
f1(n);
f1(0xffffffff);
f1(1);
}
}
}
[예제10]
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 4;
a = a + 3;
a += 3; // 복합대입연산자
//
a++;
++a; // 선호된다(stl에서는 Iterator가 10배가량 빠른 문법 이기 때문에)
a = a + 1; // add(+) mov(=)
a += 1; // 컴파일이 빠르다.
a = +1;
a = -1;
//
a = a << 3;
a <<= 3;
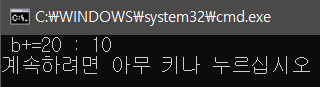
int b = 10;
WriteLine($" b+=20 : {b}");
}
}
}
[예제11]
a가 null이면 100을 출력, 그렇지 않으면 a가 가진 값을 출력한다.
using System;
using static System.Console;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
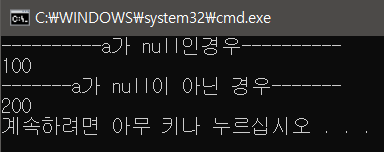
//a가 null이면 100을 출력, 그렇지 않으면 a가 가진 값을 출력하겠다.
int? a = null;
WriteLine("----------a가 null인경우----------");
WriteLine(a ?? 100);
WriteLine("-------a가 null이 아닌 경우-------");
a = 200;
WriteLine(a ?? 100);
}
}
}
728x90
반응형
'Education > Edu | .net' 카테고리의 다른 글
| # 25.1) [C#] 문법4 (0) | 2021.02.18 |
|---|---|
| # 24.2) [C#] 문법3 (0) | 2021.02.17 |
| # 23) [C/C++] 천 단위마다 "," 찍어서 출력하는 코드 (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| # 22.2) [C#] 문법1 (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| # 22.1) [C#] 시작하기2 (0) | 2021.02.16 |